What Is the Proxy?
It is a common need to share data between software systems via HTTP based APIs, but what if the HTTP request requires a piece of sensitive data that you have tokenized and do not want to access directly within your application?
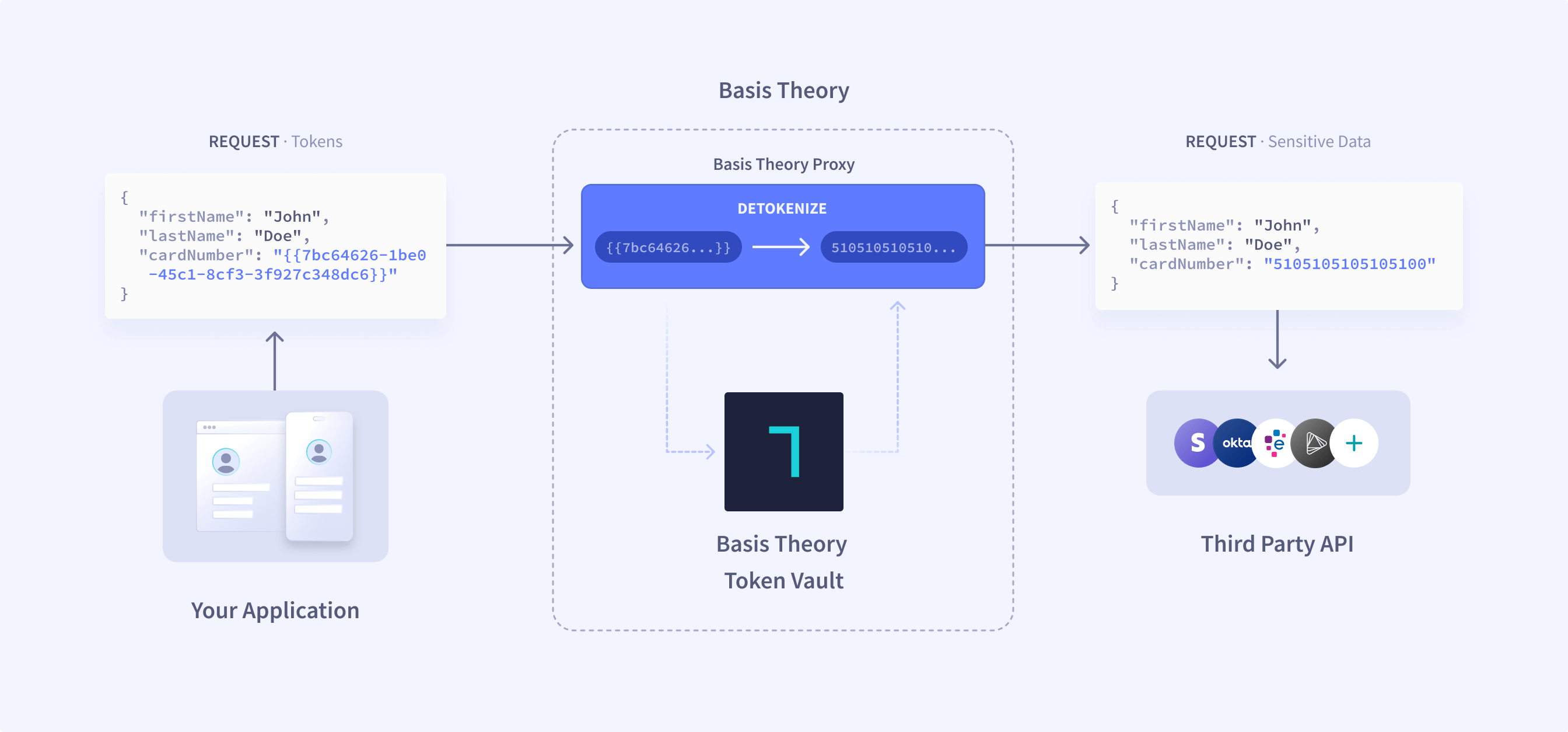
The Proxy enables you to build HTTP requests containing sensitive tokenized data and send them from your systems in a secure and compliant manner without needing to access raw token data. Your application can include token identifiers within the request payload and send this request through Basis Theory's systems to substitute token data into the request before forwarding it to the desired destination.
The end result is that you can call HTTP APIs with tokenized data without needing to touch the underlying sensitive data directly within your systems.
How It Works
Your system initiates an outbound HTTP request to the Proxy hosted by Basis Theory.
The request is transformed by evaluating any expressions included in the request (patterns of the form {{<tokenId>}}, where <tokenId> is the id of a token created within your tenant). Any detokenization expressions will be replaced with the detokenized data value of this token.
Finally, the request is delivered to the destination URL that was specified through a BT-PROXY-URL HTTP header.
The Proxy terminates the inbound TLS connection from your servers and initiates a new TLS connection to the destination in order to guarantee secure transmission of your sensitive token data.
For this reason, we require the destination servers to support TLSv1.2+ and that the provided destination URL uses https.
The application that is being used to call the Proxy must be granted token:use permission on any tokens that are detokenized.
It is recommended that you restrict which tokens the Proxy can detokenize by only granting token:use
permission on the most-specific container of tokens that is required.
Whatever the content type or HTTP method, any HTTP request can be sent through the proxy simply by adding the headers BT-API-KEY and BT-PROXY-URL. For example:
curl "https://api.basistheory.com/proxy" \
-H "BT-API-KEY: key_NS21v84n7epsSc5WzoFjM6" \
-H "BT-PROXY-URL: https://my-destination-api.com" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X "POST" \
-d '{
"sensitive": "{{e51b0ff4-aa80-407a-b628-3909c26ff397}}",
"nonSensitive": "plaintext data can go here"
}'
For further details about how to use the Proxy, check out our docs.
Common Use Cases
Share Sensitive Data with a Third Party
Tokenized data can be included in any HTTP request to a third party API by executing the HTTP request through the Proxy. This makes it easy to share sensitive data with a third party without needing to first retrieve and manipulate this sensitive data on your servers.
Upgrade an Existing System
In existing systems with sensitive data you wish to secure, this data can be migrated and tokenized with Basis Theory. Once safely tokenized, your systems still need to utilize this data with your existing HTTP calls without pulling the raw values back into your system. For this, you can leverage the Proxy in order to minimize the impact of this change on your existing codebase.
Samples
Use Token Data in HTTP Requests
FAQs
How to Choose Between the Proxy and Serverless Reactors
Basis Theory offers a number of out-of-the-box integrations to share your tokenized data with Third Party systems via our Serverless Reactor platform.
However, you may require an integration that is not yet supported, in which case you have a few options to choose from:
- Create a custom Reactor Formula containing the code required to integrate with the third party system (our serverless platform executes this code)
- Use the Proxy to send the API request from your own application (your servers execute this code)
Using the Proxy can provide a quicker and lower configuration option for making custom HTTP requests to a third party API than writing and maintaining a custom reactor formula.